Abortion is a common health intervention, with around 73 million induced abortions taking place worldwide each year. It is a safe procedure when carried out using a method recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), but around 45% of abortions are unsafe, leading to maternal deaths and morbidities. The issue of abortion is a highly divisive topic, with those in support of abortion law citing bodily autonomy and reproductive justice, while those against often cite religious and moral beliefs.
Public opinion on abortion varies depending on factors such as religious affiliation, political ideology, gender, race, and education level. For example, in the United States, Democrats are more likely than Republicans to support the legalization of abortion, with 42% of Democrats surveyed in 2024 supporting legalization under any circumstance, compared to only 6% of Republicans.
The debate around abortion law is complex and multifaceted, with a range of legal, social, cultural, and ethical considerations at play. Ultimately, the discussion centers around the question of whether abortion should be treated as a fundamental human right or as a criminal act.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Political Party | Democrats, Democratic-leaning independents, liberal Democrats, moderate and liberal Republicans |
| Religious Affiliation | Religiously unaffiliated, Black Protestants, White nonevangelical Protestants, Catholics |
| Age | Adults under 30 |
| Education Level | College graduates |
What You'll Learn

The right to bodily autonomy
Restricting access to abortion violates the right to bodily autonomy. Criminalisation of abortion, as seen in some countries, forces individuals to resort to unsafe procedures, often with fatal consequences. It infringes on their ability to make decisions about their bodies and health, imposing external control over their lives.
Additionally, social stigma, intersectional discrimination, and marginalisation create further barriers to accessing safe abortions. These obstacles disproportionately impact individuals from historically marginalised communities, hindering their ability to exercise reproductive autonomy.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recognises abortion as a simple healthcare intervention that can be safely managed by a range of health workers. When performed following WHO guidelines, abortion is one of the safest medical procedures. Restrictive abortion regulations not only violate bodily autonomy but also endanger the lives and well-being of those seeking abortions.
To respect and protect the right to bodily autonomy, it is imperative to remove legal and social barriers to abortion. This includes decriminalising abortion, addressing stigma, and ensuring universal access to safe, timely, affordable, and respectful abortion care. By upholding the right to bodily autonomy, we empower individuals to make informed decisions about their bodies and futures, free from external coercion or control.
Indiana's Abortion Trigger Law: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

The right to life, health, and freedom from cruel treatment
Abortion is a highly debated topic, with varying opinions across the world. The right to life, health, and freedom from cruel treatment are fundamental human rights that are often discussed in the context of abortion laws. Here are some perspectives on how these rights relate to the issue:
Right to Life
The right to life is a fundamental human right, and it is often cited in the context of abortion debates. Those who oppose abortion laws often argue that abortion violates the right to life of the fetus. They believe that life begins at conception and, therefore, terminating a pregnancy is equivalent to taking a life. This perspective is influenced by religious and moral beliefs, which vary across different societies and cultures.
On the other hand, proponents of abortion rights argue that abortion is a necessary healthcare procedure that can save lives. They emphasize that unsafe abortions, often resulting from restrictive laws, pose significant risks to the life and health of pregnant individuals. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), comprehensive abortion care, including safe and effective medical or surgical procedures, is essential to protecting the lives of those who can become pregnant.
Right to Health
The right to health is another crucial aspect of the abortion debate. Restrictive abortion laws can negatively impact the physical and mental health of pregnant individuals. Lack of access to safe and legal abortion services can lead to unsafe abortion practices, increasing the risk of physical complications and mental health issues. Additionally, the stigma associated with abortion further exacerbates the risks to the well-being of those seeking abortions.
Proponents of abortion rights advocate for the inclusion of comprehensive abortion care within essential health care services. They argue that abortion should be recognized as a simple healthcare intervention that can be safely managed by a range of health workers. By ensuring access to accurate information, quality medications, and supportive health workers, the risks associated with abortion can be minimized.
Freedom from Cruel Treatment
The debate around abortion also raises questions about freedom from cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment. Restrictive abortion laws can result in distress and stigma for those seeking abortions. The criminalization of abortion and the involvement of law enforcement can create a hostile environment, deterring individuals from seeking safe abortion services. Additionally, such laws can lead to unsafe abortion practices, causing physical and mental health complications, social isolation, and financial burdens.
Proponents of abortion rights argue that abortion should be treated as any other form of healthcare, with best practices in service delivery, provider training, and evidence-based guidelines. They emphasize that abortion-related decisions should belong solely to the pregnant individual, without interference from the state or legal system.
In conclusion, the right to life, health, and freedom from cruel treatment are integral to the abortion debate. Proponents of abortion rights advocate for safe, legal, and accessible abortion services, while opponents often cite religious and moral beliefs to support their position. The varying perspectives on these fundamental human rights continue to shape the discussion around abortion laws worldwide.
Ohio Abortion Laws: Rape, Incest, and Exclusion
You may want to see also

Preventing unsafe abortions
Unsafe abortions are a critical public health and human rights issue, causing maternal deaths, disabilities, and other morbidities. Preventing unsafe abortions requires addressing the underlying causes that drive women to seek unsafe procedures. Here are some strategies to prevent unsafe abortions and protect women's health and rights:
Reduce Unwanted Pregnancies
The first strategy is to reduce the incidence of unwanted pregnancies. This can be achieved through various measures such as:
- Improving access to effective contraception: Ensure a reliable supply of quality, affordable contraceptives and provide comprehensive sexuality education to help individuals make informed decisions.
- Post-abortion family planning counselling: Offer counselling services to individuals who have undergone abortions to help them make informed choices about future pregnancies and contraceptive methods.
- Health education campaigns: Promote condom use among young people and encourage safe sexual practices to reduce the risk of unintended pregnancies.
- Involving men in family planning: Engage men in decision-making processes regarding family planning and contraceptive use to promote shared responsibility.
- Biomedical research: Invest in research to develop safer and more effective male and female contraceptive methods.
- Empowering women: Support and educate women to demand the use of protection, such as condoms, and to avoid unwanted intercourse.
Improve Clinical Management
The second strategy focuses on reducing abortion-related mortality and morbidity by improving the clinical management of incomplete illegal abortions. This includes:
- Introducing menstrual regulation services: Provide services that help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce the risk of unintended pregnancies.
- Forming women's solidarity groups: Establish support groups to discourage the practice of self-induced abortion and provide alternatives.
- Legalising abortion: Ultimately, removing legal barriers and ensuring safe and legal access to abortion services can significantly reduce unsafe procedures and their consequences.
Address Social and Cultural Barriers
Unsafe abortions are often driven by social and cultural barriers, including criminalisation, restrictive laws, and stigma. It is essential to address these barriers through policy changes and community engagement:
- Respect for human rights: Create a supportive framework of laws and policies that respect individuals' rights to privacy, bodily autonomy, and reproductive autonomy.
- Availability and accessibility of information: Ensure that individuals have access to accurate, non-biased, and evidence-based information on abortion, contraceptive methods, and sexual health.
- Supportive health system: Develop a universally accessible, affordable, and well-functioning health system that provides a range of abortion care services, including medical and surgical procedures, without discrimination or judgment.
- Protect health workers: Support and protect health workers from stigma and ensure they are trained to provide safe and respectful abortion care, regardless of their personal beliefs.
International Support and Collaboration
International organisations, such as Amnesty International and the World Health Organization (WHO), play a crucial role in preventing unsafe abortions. These organisations can provide technical support, develop guidelines, and advocate for reproductive rights globally. WHO, for example, maintains the Global Abortion Policies Database, offering comprehensive information on abortion laws and policies worldwide. By collaborating with these organisations and utilising their resources, countries can improve their understanding of effective practices and implement evidence-based policies to prevent unsafe abortions.
New York Abortion Law: Understanding the Recent Changes
You may want to see also

Reducing maternal deaths
Abortion laws have a direct impact on maternal deaths, with restrictive abortion laws and policies contributing to higher rates of maternal mortality. Here are four to six paragraphs on how abortion law reform can help reduce maternal deaths:
Unsafe abortions are a leading cause of maternal deaths worldwide. When people are denied access to safe and legal abortion services due to restrictive laws, criminalisation, or social stigma, they often resort to unsafe abortion methods. This includes seeking abortions from untrained individuals, using dangerous and invasive methods, or self-managing abortions without proper medical supervision. These unsafe practices can lead to severe physical and mental health complications, including incomplete abortions, heavy bleeding, uterine perforation, and damage to internal organs.
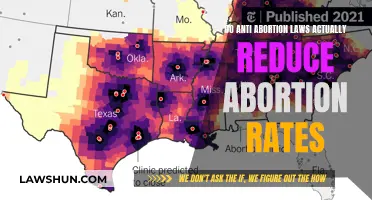
Abortion law reform is crucial to reducing maternal deaths. Evidence shows that restrictive abortion laws do not decrease the number of abortions but instead make them less safe and more dangerous for pregnant individuals. By contrast, countries with less restrictive abortion laws tend to have lower maternal mortality rates. Liberalising abortion laws can help ensure that abortions are performed safely and effectively by trained health workers using recommended methods, reducing the risk of complications and death.
The impact of abortion law reform is evident in countries that have made changes. For example, in Argentina, legalising abortion resulted in a notable decrease in maternal mortality. Similarly, Nepal's abortion law reform, which allowed abortion for rape or incest, physical or mental health reasons, was associated with a significant decline in abortion-related morbidities. These reforms not only reduce maternal deaths but also improve overall maternal health outcomes.
Abortion education and training for medical professionals are essential to reducing maternal mortality. Restrictive abortion laws limit medical students' and residents' access to abortion education, compromising the quality of obstetric care. By incorporating comprehensive abortion education into medical school curricula, future physicians will be better equipped to provide safe and legal abortions as part of essential healthcare. This includes training in counselling, medication abortion, and surgical abortion methods.
Additionally, addressing systemic racism and sexism in medical education is vital. The exclusion of people of colour from the medical profession has led to a lack of culturally concordant care, further exacerbating racial inequities in maternal health. Increasing diversity among healthcare providers and improving cultural competence can help reduce disparities and improve health outcomes for underserved communities.
Finally, it is important to recognise that abortion law reform alone may not be sufficient to reduce maternal deaths immediately. It must be accompanied by improved access to safe abortion services and a reduction in the stigma surrounding abortion. Public awareness campaigns about changes in abortion laws and the availability of safe abortion services are crucial to ensuring that individuals know their rights and can access the care they need.
Texas Abortion Law: Who Authored the Controversial Legislation?
You may want to see also

Protecting reproductive justice
Reproductive justice is an important concept that recognises the intersection of gender equality, sexual and reproductive rights, and social justice. It addresses issues such as population control, bodily self-determination, immigrants' rights, economic and environmental justice, sovereignty, and criminal injustices that limit individual human rights due to group or community oppressions. Protecting reproductive justice is essential to ensuring that individuals have the right to control their fertility and exercise reproductive autonomy. Here are some ways to protect reproductive justice:
Address Social, Economic, and Political Inequalities
Reproductive justice demands that states address social, economic, and political inequalities that prevent people, especially those from marginalised communities, from exercising their sexual and reproductive rights. This includes ensuring access to comprehensive sexuality education, modern contraception, and safe abortion services. It also means addressing restrictive laws and requirements that are not medically justified, such as criminalisation of abortion, mandatory waiting periods, and biased counselling.
Ensure Safe and Accessible Abortion Services
Abortion is a common and safe health intervention when carried out using methods recommended by the World Health Organisation (WHO). However, when people face barriers such as criminalisation, stigma, and high costs, they often resort to unsafe abortions, which can lead to physical and mental health complications and even death. Comprehensive abortion care should be included in essential health care services, with a range of approaches such as care in health facilities, digital interventions, and self-care methods.
Respect Human Rights and Provide Supportive Policies
Empower Marginalised Communities
Particular attention should be given to marginalised communities, including low-income individuals, refugees, migrants, LGBTIQA+ people, racialised and Indigenous people, and those from historically marginalised groups. These communities often face additional barriers to accessing abortion services due to health service inaccessibility, social stigma, and intersectional discrimination. Efforts to improve access to abortion must consider the unique needs of these communities and address the social, cultural, and economic barriers they face.
Provide Accurate Information and Contraception
Availability and accessibility of information are crucial. Evidence-based comprehensive sexuality education and accurate, non-biased information on abortion and contraceptive methods should be provided to the public. Additionally, ensuring access to a range of contraceptive options can help reduce the number of unintended pregnancies and the need for abortions.
Collaborate with Allies
Achieving critical mass support from allies is vital for successful law reform to protect reproductive justice. This includes parliamentarians, health professionals, legal experts, women's groups, human rights organisations, and family planning supporters. Working together, this coalition can advocate for laws and policies that truly benefit women and ensure their reproductive rights.
Alabama's Abortion Law: Plan B Pill's Future
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Support for abortion law is generally higher among Democrats and those who are not affiliated with any religion.
Majorities of both men (61%) and women (64%) express support for legal abortion.
Support for abortion law is higher among Black (73%) and Asian (76%) adults compared with White (60%) and Hispanic (59%) adults.
Support for abortion law is higher among younger people, with 76% of adults under 30 saying abortion should be legal, compared to 61% of adults in their 30s and 40s.
Support for abortion law is higher among those with a college education (68%) compared to those with a high school education or less (56%).