Moore's Law, named after Intel co-founder Gordon Moore, states that the number of transistors on a microchip will double approximately every two years, leading to exponential growth in computing power. This has had a profound impact on artificial intelligence (AI), as the increased processing power has enabled significant advances in AI technology, particularly in machine learning and deep learning. However, some argue that Moore's Law will eventually reach its limits, leading to a slowdown in AI development. Nevertheless, the rapid progress in AI has raised questions about its potential impact on society, including the creation of wealth, the distribution of wealth, and the future of labour.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Moore's Law | The number of transistors on a microchip will double every two years |
| The cost of computers will halve every two years | |
| Impact on AI | AI has seen rapid progress due to Moore's Law |
| AI applications can be built into smaller devices | |
| AI can process more data faster | |
| Moore's Law has allowed AI to make significant advances | |
| Moore's Law has driven technological advancements for over 50 years | |
| Limitations of Moore's Law | Moore's Law will eventually reach its limits |
| Moore's Law does not apply to deep learning | |
| Alternative Technologies | Quantum computing |
| Neural networks | |
| Generative AI |
What You'll Learn

Moore's Law and AI hardware
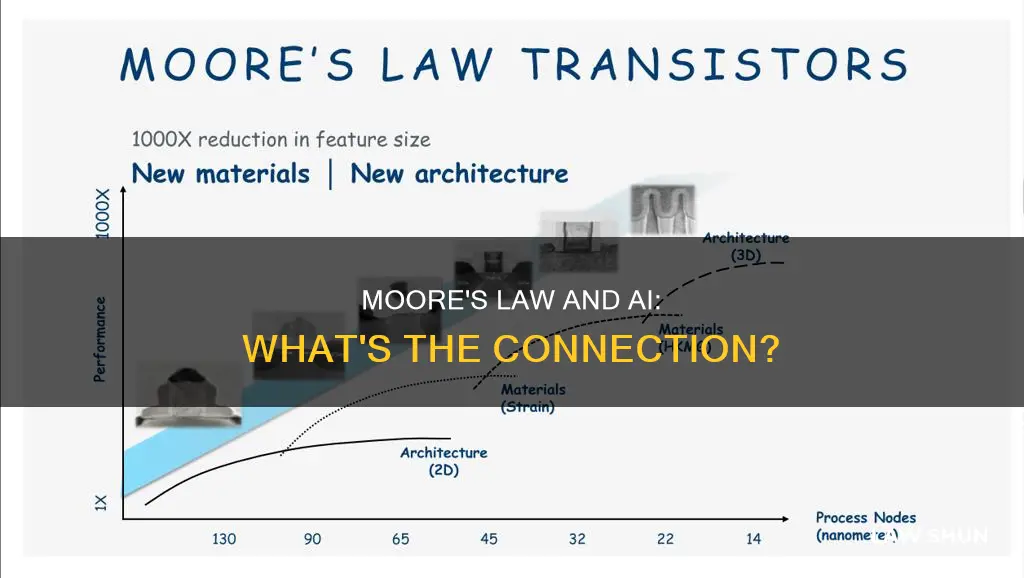
Moore's Law, formulated by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore, predicts that the number of transistors on a microchip will double about every two years, while the cost of computers will halve. This "law" has been a guiding principle for the tech industry for decades, with Moore's Law essentially telling us that our devices will get faster, smarter, and cheaper at a predictable pace.
The exponential improvement in computer hardware performance over the last few decades, as described by Moore's Law, has had a profound impact on artificial intelligence (AI). As computer hardware continued to improve at an exponential rate, AI researchers were able to start building systems that could approach human levels of intelligence. This breakthrough led to the rapid expansion of machine learning, a subset of AI that has led to the development of many successful applications such as self-driving cars and digital assistants.
Moore's Law has enabled the creation of more powerful and efficient computing hardware, which is essential for AI development. The ever-increasing processing power made available by Moore's Law has allowed AI to make significant advances, particularly in the data-hungry computing requirements of deep learning systems. AI applications can now be built into ever-smaller devices, making them more accessible and affordable.
However, some believe that Moore's Law will eventually reach its limits, leading to a slowdown in AI development. The physics of putting more transistors on a chip and managing the heat created by new chips has slowed the performance enhancements of individual chips. Additionally, quantum computing and software advancements in machine learning, neural networks, and generative AI are also playing an increasingly important role in enhancing AI capabilities, separate from the predictions of Moore's Law.
While it is difficult to identify a single law or principle that governs AI advancement, the field is constantly evolving, and AI progress will undoubtedly be much faster than we can imagine.
Administrative Law: Beyond Traffic Violations?
You may want to see also

Moore's Law and AI software
Moore's Law states that the number of transistors on a microchip will double every two years, leading to exponential growth in computing power. This has been a driving force behind technological advancements for over 50 years, and has had a profound impact on artificial intelligence (AI). The exponential improvement in computer hardware performance has allowed AI researchers to build systems that can approach human levels of intelligence, leading to the rapid expansion of machine learning and the development of many successful applications.
AI is particularly well-suited to taking advantage of the continued exponential growth in computing power predicted by Moore's Law. AI requires massive amounts of data and computing power to train its algorithms. As chips continue to get smaller and more powerful, AI will become even more ubiquitous and influential. Moore's Law has acted as a beacon for the tech industry's progress, and its impact on society has been profound. The exponential increases in computing power have driven economic growth, transformed entire industries, and improved the lives of billions of people worldwide.
However, it's important to note that Moore's Law focuses on the scale-up of computing power, rather than the scale-out that is more relevant to deep learning and AI. The physics of putting more transistors on a chip and managing the heat created by new chips has led to a slowdown in performance enhancements. What really changed things for AI was networking—the ability to coordinate multiple servers for a single task, which massively improved performance for many applications, including deep learning.
While Moore's Law has played a significant role in the development of AI, it's difficult to identify a single law or principle that governs AI advancement. The field is constantly evolving and is driven by a variety of factors, including technological advancements, breakthroughs in research, and market demand. Quantum computing, for example, holds a lot of promise for enhancing AI capabilities much faster than traditional computing. Additionally, software advancements such as machine learning, neural networks, and generative AI are also crucial to the progress of AI.
Consumer Law: Who Does It Protect?
You may want to see also

Moore's Law and AI training
Moore's Law states that the number of transistors on a microchip will double every two years, leading to exponential growth in computing power. This has been a driving force behind technological advancements for over 50 years and has had a profound impact on artificial intelligence (AI). The exponential improvement in computer hardware performance enabled by Moore's Law has allowed AI researchers to build systems that can approach human levels of intelligence, leading to the rapid expansion of machine learning and the development of applications such as self-driving cars and digital assistants.
AI training is outpacing Moore's Law, with improvements to software and processor and computer architecture resulting in significant speedups for AI training performance. For example, the gains in AI training performance since the early version of the MLPerf benchmarks outstripped the increase in transistor density predicted by Moore's Law. This highlights the importance of software advancements and processor and computer architecture in addition to hardware improvements in driving AI progress.
While Moore's Law has been a significant factor in the development of AI, it is not the only factor governing AI advancement. The field of AI is constantly evolving and is influenced by a variety of factors, including technological advancements, breakthroughs in research, and market demand. Quantum computing, for instance, holds promise for enhancing AI capabilities much faster than traditional computing. Additionally, software advancements such as machine learning, neural networks, and generative AI have accelerated AI development.
The exponential growth of AI has been further accelerated by the convergence of affordable computing power, the deluge of data, and significant capital investment. This has led to the birth of new neural networks and innovative architectures that learn and adapt in ways previously unimaginable. AI's computational power is doubling approximately every six months, reshaping what is possible for organizations and society as a whole.
Open Container Laws and RVs: What's the Verdict?
You may want to see also

Moore's Law and AI data
Moore's Law, formulated by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore, predicts that the number of transistors on a microchip will double about every two years, while the cost of computers will halve. This has remarkably held true for decades, acting as a beacon for the tech industry's progress. Moore's Law has been one of the driving forces behind the development of AI, as it has enabled the creation of more powerful and efficient computing hardware. The exponential improvement in computer hardware performance has allowed AI researchers to build systems that can approach human levels of intelligence, leading to the rapid expansion of machine learning and the development of applications such as self-driving cars and digital assistants.
However, it is important to note that Moore's Law only deals with the scale-up of computing power on a single chip. The physics of putting more transistors on a chip and managing the heat created by new chips has led to a slowdown in performance enhancements. On the other hand, networking and communications between computers and their components have continued to improve, enabling parallel processing and cloud computing. This is known as scale-out, and it is what is currently pushing forward the frontiers of AI.
While Moore's Law has had a significant impact on AI, the field of AI is constantly evolving and is influenced by a variety of factors. Quantum computing, for example, holds promise for enhancing AI capabilities much faster than traditional computing. Additionally, software advancements such as machine learning, neural networks, and generative AI are also playing a crucial role in accelerating AI development.
The exponential growth of AI has been further accelerated by the convergence of affordable computing power, the deluge of data, and significant capital investment. This has led to the birth of new neural networks and innovative architectures that can learn and adapt in ways previously unimaginable. As a result, AI has made monumental strides in fields such as image recognition, language understanding, and reading comprehension.
In conclusion, while Moore's Law has been a key factor in the development of AI, the field of AI is influenced by a multitude of factors and technologies. The exponential growth of AI is a result of the convergence of computing power, data, and investment, and it continues to reshape what is possible for organizations and society as a whole.
Understanding California Employment Laws: Statutory Employees
You may want to see also

Moore's Law and the future of AI
Moore's Law, named after Intel co-founder Gordon Moore, states that the number of transistors on a microchip will double approximately every two years, leading to exponential growth in computing power. This law has been a driving force behind technological advancements for over 50 years and has had a profound impact on artificial intelligence (AI). As a result, AI has seen rapid progress, with machine learning expanding rapidly and leading to the development of applications such as self-driving cars and digital assistants.
The exponential improvement in computer hardware performance, as predicted by Moore's Law, has allowed AI to make significant advances. The ever-increasing processing power has enabled AI to handle the data-hungry computing requirements of deep learning systems. However, there are still challenges to be overcome for AI to reach its full potential. While Moore's Law may eventually reach its limits, alternative technologies like quantum computing offer the potential for continued indefinite improvement.
AI is particularly well-suited to benefit from Moore's Law as it requires massive amounts of data and computing power to train its algorithms. As chips continue to become smaller and more powerful, AI will become even more ubiquitous and influential. The potential for AI increases as electronic devices get more powerful, allowing AI applications to be built into smaller devices and making them more accessible and affordable. Additionally, with more processing power, devices can handle larger datasets, which is crucial for machine learning.
The impact of Moore's Law on society has been far-reaching, driving economic growth, transforming industries, and improving lives worldwide. As transistor counts continue to increase, the potential for AI applications grows as well. This continued miniaturization of transistors enables more powerful AI applications by providing the necessary data processing capacity and physical space for AI hardware. As a result, we can expect even more transformative changes in the years ahead.
However, it's important to recognize that Moore's Law won't last forever. While it has held for over 50 years, there are signs of it slowing down, such as processor speeds plateauing. Nevertheless, even if Moore's Law ends, its impact will persist, and its legacy will continue to shape the future of AI and cutting-edge technologies.
HIPAA Laws: Do Private Citizens Need to Comply?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Moore's Law states that the number of transistors on a microchip will double every two years, leading to exponential growth in computing power.
Moore's Law has been one of the key reasons for the rapid progress in AI in recent years. The law has allowed for significant advances in AI, due to the data-hungry computing requirements of deep learning systems.
Some believe Moore's Law will eventually reach its limits. However, others believe that alternative technologies, such as quantum computing, will allow it to continue indefinitely.