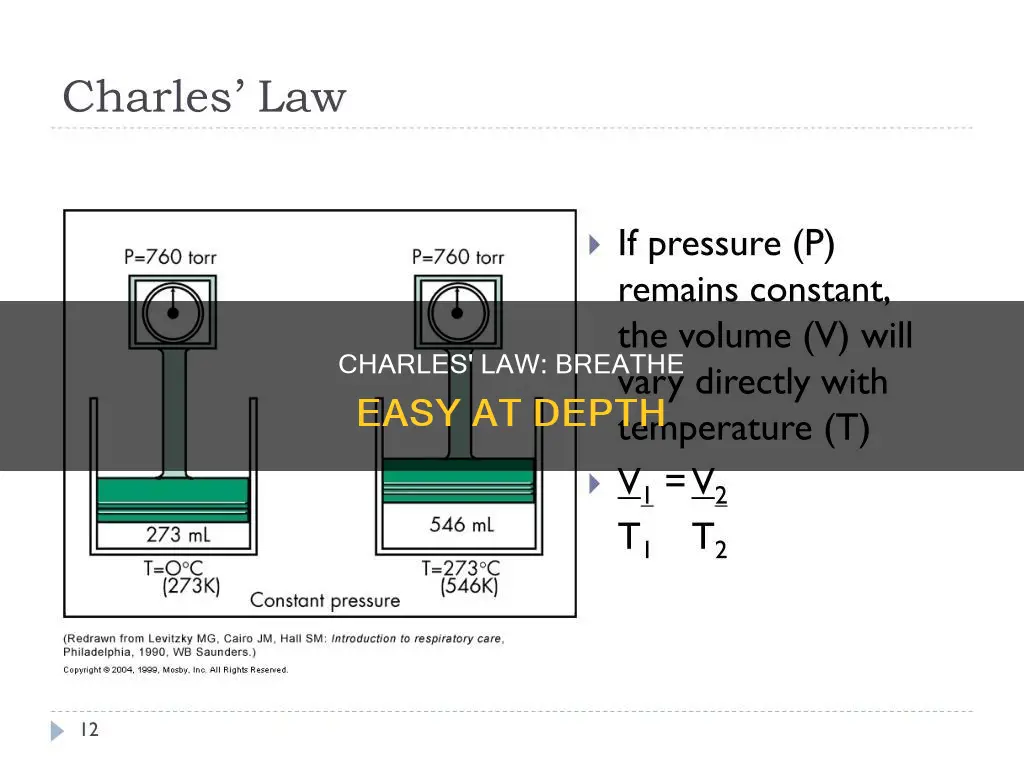
Charles's Law, also known as the law of volumes, is a gas law that explains the relationship between the temperature of a gas and its volume. The law states that when the pressure on a sample of dry gas remains constant, the Kelvin temperature and the volume are in direct proportion. In other words, as the temperature of a gas increases, so does its volume, and vice versa. This law was formulated by scientist Jacques Charles in the 1780s and later confirmed by French naturalist Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac. While Charles's Law is the least applicable of the gas laws when it comes to respiration, as body temperature rarely fluctuates, it does have an impact on breathing. When we inhale cold air, it expands as it warms in our sinuses and lungs, affecting the volume of air we can inhale.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| How does Charles's Law apply to breathing? | It affects the volume of air you can inhale. |
| When you inhale cold air, it will change volume as it warms in passing through the sinuses. | |
| As the air warms, it expands to a larger volume. | |
| Charles's Law does not affect breathing as much as Boyle's Law. | |
| Volume and temperature relationship | When the pressure on a sample of dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion. |
| The volume of a gas increases as the temperature increases. | |
| A decrease in temperature will lead to a decrease in volume. | |
| The volume of a fixed mass of dry gas increases or decreases by 1/273 times the volume at 0°C for every 1°C rise or fall in temperature. | |
| Applicability | Charles's Law is the least applicable to respiration since body temperature rarely changes by much. |
What You'll Learn

Charles' Law and the volume of air inhaled
Charles's Law, also known as the law of volumes, is an experimental gas law that explains how gases tend to expand when heated. The law states that when the pressure on a sample of dry gas remains constant, the Kelvin temperature and volume are directly proportional. This means that as the temperature of the gas increases, so does its volume.
The law can be written as:
V ∝ T
Or
V = kT
Where V is the volume of the gas, T is the temperature of the gas (measured in Kelvins), and k is a constant for a particular pressure and amount of gas.
The law can also be written in the following form to compare the same substance under two different sets of conditions:
V1/T1 = V2/T2
This equation shows that as the absolute temperature increases, the volume of the gas also increases proportionately.
Charles's Law affects the volume of air inhaled. When we breathe in cold air, it changes volume as it warms when passing through the sinuses. As the air warms, it expands to a larger volume. For example, if the outside temperature is -10°C, the inhaled air will expand as it reaches the temperature in our lungs (37°C).
Charles's Law is less applicable to respiration than Boyle's Law or Dalton's Law because body temperature rarely fluctuates significantly.
Joshua Law: Applicability to 17-Year-Olds Explored
You may want to see also

How the law affects breathing
Charles's Law, also known as the law of volumes, is a gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. It states that when the pressure on a sample of dry gas remains constant, the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion. This means that as the temperature of the gas increases, so does its volume.
In the context of breathing, Charles's Law affects the volume of air inhaled. When we breathe in cold air, it will change volume as it warms when passing through the sinuses and into the lungs. As the air warms, it expands to a larger volume. For example, if the outside temperature is -10°C, the inhaled air will expand as it reaches the temperature in our lungs (37°C).
Charles's Law is less applicable to breathing than other gas laws like Boyle's Law and Dalton's Law because body temperature usually doesn't fluctuate much. However, it does have an effect on the volume of air we inhale, especially in colder temperatures.
Livestream Wiretapping: California's Unique Legal Perspective
You may want to see also

The impact of temperature on breathing
Charles's Law, also known as the law of volumes, states that when the pressure on a sample of dry gas remains constant, the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion. In other words, as the temperature of a gas sample is increased, its volume increases, and vice versa. This law was formulated by scientist Jacques Charles in the 1780s.
Charles's Law affects the volume of air we inhale. When we breathe in cold air, it expands as it warms in our sinuses and travels through our respiratory system. This means that the volume of cold air we inhale will be larger than the volume of that same air once it has warmed to our body temperature. For example, if the outside temperature is -10°C, and the temperature in our lungs is 37°C, we would have to inhale 420 mL of cold air to make a volume of 500 mL at 37°C. As a result, we tend to take shorter breaths in cold weather.
Charles's Law is less applicable to breathing than other gas laws, such as Boyle's Law, as body temperature does not fluctuate much. However, it is important to consider the impact of temperature on the volume of air we inhale, particularly in extremely cold or hot conditions.
In summary, Charles's Law describes the relationship between the temperature and volume of a gas. It explains how the volume of air we inhale changes as it warms or cools within our respiratory system, depending on the external temperature.
Lemon Law: Private Sales in Texas Explained
You may want to see also

The relationship between temperature and volume
Charles's Law, also known as the Law of Volumes, is an experimental gas law that describes the relationship between temperature and volume. It states that when the pressure on a sample of dry gas remains constant, the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion. In other words, as the temperature of a gas increases, so does its volume, and conversely, a decrease in temperature leads to a decrease in volume.
The relationship can be written as:
V ∝ T
Or
V = kT
Where V is the volume of the gas, T is the temperature of the gas (measured in Kelvins), and k is a constant for a particular pressure and amount of gas.
The law can also be written as:
V1/T1 = V2/T2
This equation shows that as the absolute temperature (T) increases, the volume (V) of the gas also increases in proportion.
For example, if you inhale cold air, it will change volume as it warms when passing through the sinuses and into the lungs, which have a higher temperature. As the air warms, it expands to a larger volume.
Charles's Law is named after scientist Jacques Charles, who formulated the original law in his unpublished work from the 1780s. However, it should be noted that Charles's Law is less applicable to breathing than other gas laws like Boyle's Law and Dalton's Law since body temperature rarely fluctuates significantly.
Zoning Laws and Private Roads: Who's in Control?
You may want to see also

How the law compares to Boyle's Law
Charles's Law and Boyle's Law are two of the simple gas laws that describe the relationships between the pressure (P) of a gas and its volume (V), temperature (T), and amount (n).
Charles's Law states the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas. It can be written as:
$$V \propto T$$
This means that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature (in kelvins) when the pressure and amount of gas remain constant. In other words, as the temperature of a gas increases, so does its volume, and vice versa. This law is named after the French chemist Jacques Alexandre César Charles, who conducted experiments in 1783 that revealed this relationship.
On the other hand, Boyle's Law describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas. It can be written as:
$$P \propto \frac{1}{V}$$
This equation shows that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume when the temperature and amount of gas remain constant. Therefore, when the volume of a gas decreases, its pressure increases, and vice versa. This law is named after the Irish chemist Robert Boyle, who performed experiments in the 17th century that established this relationship.
In summary, the key differences between Charles's Law and Boyle's Law are:
- Charles's Law relates volume and temperature, while Boyle's Law relates pressure and volume.
- Charles's Law describes a direct relationship between volume and temperature, whereas Boyle's Law describes an inverse relationship between pressure and volume.
- Charles's Law was formulated by Jacques Charles, and Boyle's Law by Robert Boyle.
Murphy's Law: Accessory Dwellings and Legal Implications
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Charles's Law, also known as the law of volumes, is a gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. It states that when the pressure on a sample of dry gas remains constant, the Kelvin temperature and volume of the gas will be in direct proportion.
Charles's Law affects the volume of air you can inhale. When you breathe in cold air, it will expand as it warms up in your sinuses and lungs.
No, Charles's Law has less of an impact on breathing than Boyle's Law. However, it does still have an effect, particularly when breathing in cold air.
The mathematical formula for Charles's Law is: V ∝ T, or V = kT, where V is the volume of the gas, T is the temperature in Kelvins, and k is a constant for a particular pressure and amount of gas.







