The law of conservation of mass states that mass or matter cannot be created or destroyed, though it may be rearranged and transformed from one form to another. This means that the mass of an isolated system will remain constant over time. Photosynthesis is a process that converts light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, and it follows the law of conservation of mass. During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide and water are converted into glucose and oxygen, with the number of atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen remaining the same throughout the process. This results in the total mass of the reactants (carbon dioxide and water) being equal to the total mass of the products (glucose and oxygen).
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Law of Conservation of Mass | Mass (or matter) cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed |
| Application to Photosynthesis | The number of atoms in the reactants is the same as the number in the products |
| Mass is conserved during photosynthesis |
What You'll Learn

The number of atoms in the reactants is the same as in the products
The law of conservation of mass states that the mass of a system will remain constant over time. In other words, mass cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged and changed into different types of substances. This law applies to all chemical reactions, including photosynthesis.
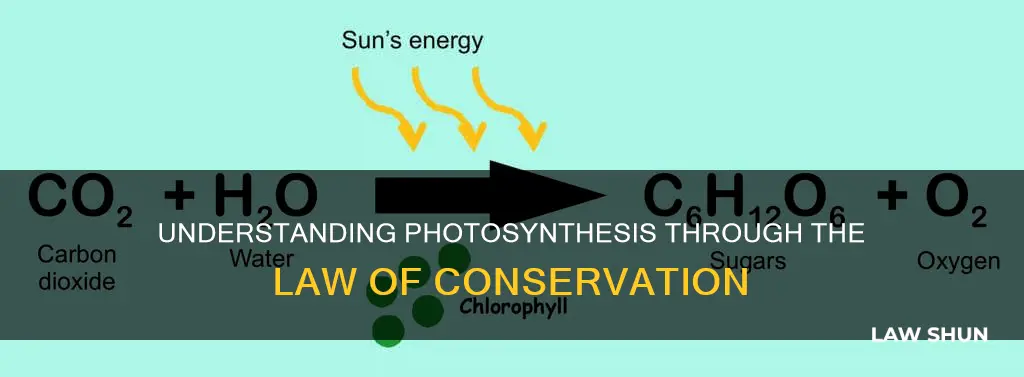
During photosynthesis, light energy is used to convert carbon dioxide and water (the reactants) into glucose and oxygen (the products). This process can be represented by the following chemical equation:
$$6\text{CO}_2 + 6\text{H}_2\text{O} + \text{light energy} \rightarrow \text{C}_6\text{H}_{12}\text{O}_6 + 6\text{O}_2$$
In this equation, there are six carbon molecules on both sides, six hydrogen molecules on both sides, and six oxygen molecules on both sides. This demonstrates that the number of atoms in the reactants is the same as in the products.
For example, the reactants include six carbon dioxide molecules, each with one carbon atom ($6\text{CO}_2$), while the products contain one glucose molecule with six carbon atoms ($\text{C}_6\text{H}_{12}\text{O}_6$). Similarly, there are twelve hydrogen atoms in the six water molecules on the reactants side ($6\text{H}_2\text{O}$) and twelve hydrogen atoms in the one glucose molecule and six water molecules on the products side ($\text{C}_6\text{H}_{12}\text{O}_6 + 6\text{H}_2\text{O}$).
Therefore, the law of conservation of mass is upheld during photosynthesis, as the number of atoms remains constant throughout the process. This conservation of atoms is essential to ensure that mass is conserved, as the mass of a substance is determined by the number and type of atoms it contains.
How Momentum is Conserved in the Universe
You may want to see also

Mass is conserved in chemical reactions
The law of conservation of mass states that mass (or matter) within a closed system remains constant over time. In other words, mass cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This is true of all chemical reactions, including photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is a process that converts light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. During this process, carbon dioxide and water are converted into glucose and oxygen. The chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
This equation demonstrates the law of conservation of mass in action. The number of atoms of each element remains the same on both sides of the equation, indicating that no atoms are lost or gained during the reaction. For example, there are six carbon molecules on both sides of the equation. The reactants include six carbon dioxide molecules, each with one carbon atom (6CO2), while the products contain one glucose molecule with six carbon atoms (C6H12O6).
Similarly, the number of hydrogen and oxygen atoms remains constant. The reactants contain 12 hydrogen atoms and 18 oxygen atoms, and the products also contain 12 hydrogen atoms and 18 oxygen atoms. Therefore, the total mass of the reactants (carbon dioxide and water) is equal to the total mass of the products (glucose and oxygen).
This conservation of mass is a fundamental principle of chemistry and is observed in all chemical reactions, including photosynthesis. It is important to note that while mass is conserved, it can change states or be rearranged into different types of substances. This principle is analogous to the law of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Colorado's Green Law: Private Wells Included?
You may want to see also

Matter can change states
The law of conservation of mass states that mass or matter cannot be created or destroyed, though it can change states and be rearranged into different substances. This is similar to the law of conservation of energy. The mass of an isolated system will remain constant over time.
The world is filled with solids, liquids, and gases, and even other states of matter that can go from one state to another without changing its chemical substance. These changes in state can be induced by extreme temperatures or pressures. For instance, oxygen (O2) will solidify at -361.8°F (-218.8°C) at standard pressure. However, if pressure is increased, it will freeze at warmer temperatures.
The chemical equation for photosynthesis demonstrates that the number of atoms in the reactants is the same as in the products. For instance, there are six carbon molecules on both sides of the equation. The reactants include six carbon dioxide molecules, each with one carbon atom (6CO2), while the products contain one glucose molecule with six carbon atoms (C6H12O6). Hence, matter is conserved during photosynthesis, as it is during all chemical reactions.
Lemon Law and Furniture: What's the Verdict?
You may want to see also

Atoms are conserved in chemical processes
The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This law applies to all chemical processes, including photosynthesis, where mass is conserved.
Photosynthesis is a process that converts light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. During this process, carbon dioxide and water are converted into glucose and oxygen. The chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
In this equation, the number of atoms of each element remains the same on both sides. There are six carbon molecules, twelve hydrogen molecules, and eighteen oxygen molecules on both sides of the equation. This demonstrates that atoms are conserved in the process of photosynthesis.
For example, the reactants include six carbon dioxide molecules, each with one carbon atom (6CO2), while the products contain one glucose molecule with six carbon atoms (C6H12O6). Therefore, the total mass of the reactants (carbon dioxide and water) is equal to the total mass of the products (glucose and oxygen).
This conservation of atoms in chemical processes is a fundamental principle of chemistry. It is tied to the law of conservation of mass because every atom contributes to the mass of reactants and products in a reaction. As a result, not losing any atoms is equivalent to not losing any mass.
In summary, the law of conservation of mass states that mass cannot be created or destroyed, and this principle applies to photosynthesis. During this process, the number of atoms of each element remains constant, demonstrating that atoms are conserved in chemical processes.
LLC Laws: Idaho vs Nevada - What's the Difference?
You may want to see also

Total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products
The law of conservation of mass states that mass or matter cannot be created or destroyed, although it may be rearranged and transformed into different types of substances. This means that the total mass of the reactants will always equal the total mass of the products.
Photosynthesis is a process that converts light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide and water are converted into glucose and oxygen. The chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
In this equation, the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. There are six carbon molecules, six hydrogen molecules, and six oxygen molecules on both sides of the equation. This means that the total mass of the reactants (carbon dioxide and water) is equal to the total mass of the products (glucose and oxygen).
For example, the reactants include six carbon dioxide molecules, each with one carbon atom (6CO2), while the products contain one glucose molecule with six carbon atoms (C6H12O6). Therefore, the total mass of carbon in the reactants is equal to the total mass of carbon in the products. The same is true for hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
This conservation of mass during photosynthesis is a result of the conservation of atoms in chemical reactions. Atoms are conserved in chemical processes, and since every atom contributes to the mass of reactants and products, not losing any atoms is equivalent to not losing any mass.
Overall, the law of conservation of mass applies to photosynthesis because the total mass of the reactants (carbon dioxide and water) is equal to the total mass of the products (glucose and oxygen).
Cell Phone Laws: Private Property Exempt?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass or matter cannot be created or destroyed, although it may be rearranged and transformed into different types of substances.
During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide and water are converted into glucose and oxygen. The number of atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen remains the same throughout the process, meaning that the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products.
The chemical equation for photosynthesis is: 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2. This equation demonstrates that the number of atoms in the reactants is the same as the number of atoms in the products, thus conserving mass.