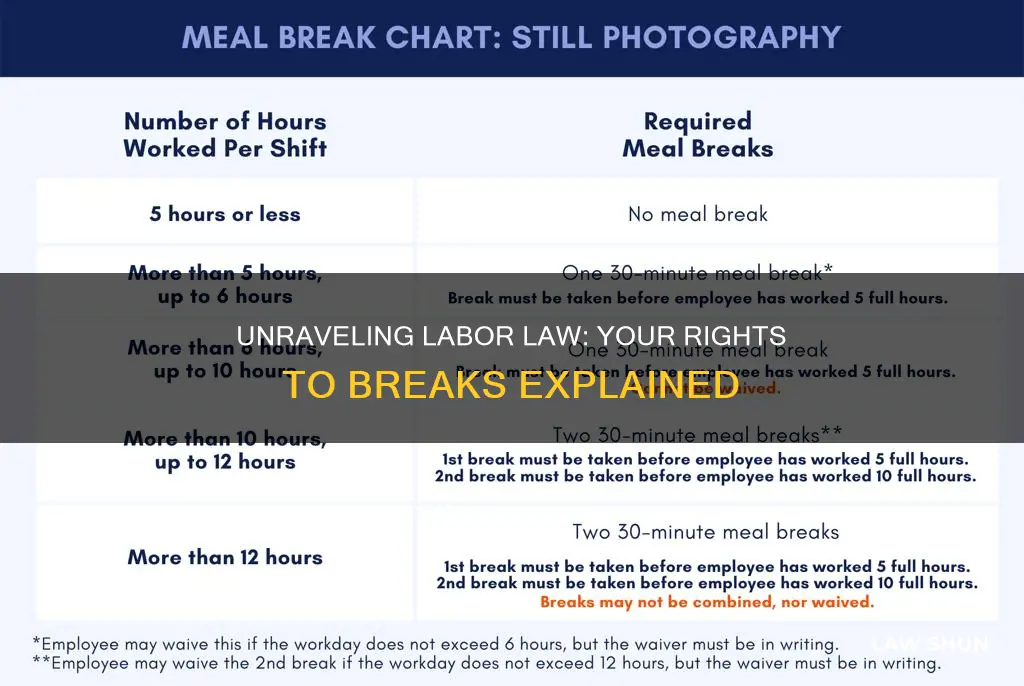
Labor law plays a crucial role in ensuring fair and safe working conditions for employees, and break times are an essential aspect of this. Understanding the legal requirements for breaks is vital for both employers and employees to maintain productivity, health, and well-being. This paragraph will explore the legal standards and regulations surrounding break times, including the duration of breaks, payment for break time, and the rights of employees to take necessary rest periods. By delving into these aspects, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the labor law framework governing breaks and its impact on the modern workplace.
What You'll Learn
- Entitlements: Workers are entitled to paid rest breaks under labor law
- Duration: Breaks must be a minimum of 10 minutes for every 4 hours worked
- Frequency: Employers must provide breaks at regular intervals throughout the workday
- Enforcement: Violations can result in legal action and penalties
- Exceptions: Certain jobs may have different break requirements or none at all

Entitlements: Workers are entitled to paid rest breaks under labor law
Workers in many jurisdictions are legally entitled to paid rest breaks as a fundamental aspect of labor law. These breaks are designed to provide employees with regular periods of rest during their work shifts, ensuring they can maintain focus, productivity, and overall well-being. The specific regulations regarding rest breaks can vary depending on the country and local labor legislation.
In many countries, labor laws mandate that employers provide workers with short breaks throughout the workday. For example, in the European Union, the Working Time Directive requires employers to grant workers a minimum of a 15-minute rest break after every 60 minutes of continuous work. This break is typically unpaid, but it is an essential component of a healthy work-life balance. However, there are also jurisdictions where paid rest breaks are the norm. In California, for instance, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and the California Labor Code both require employers to provide a 10-minute paid rest break for every 4 hours of work. This paid break is crucial as it ensures that employees are not penalized for taking time to relax and recharge, thus promoting a more sustainable work environment.
The entitlement to paid rest breaks is a significant aspect of labor law, as it directly impacts the rights and well-being of workers. These breaks are not merely a matter of convenience but are legally mandated to prevent fatigue, improve job satisfaction, and maintain the health of employees. When employers comply with these regulations, they contribute to a more productive and satisfied workforce.
It is essential for workers to be aware of their rights regarding rest breaks and to understand the labor laws in their respective regions. Employees should also be knowledgeable about the duration and frequency of breaks they are entitled to, as well as any specific requirements set by their employers. By being informed, workers can ensure that their employers adhere to the labor laws, promoting a fair and healthy work environment.
In summary, labor law recognizes the importance of rest breaks for workers' health and productivity. Paid rest breaks are a legal entitlement, ensuring employees receive necessary downtime without loss of pay. Understanding these entitlements empowers workers to advocate for their rights and maintain a balanced work-life dynamic.
Trump's Emoluments Clause Violation: What's the Verdict?
You may want to see also

Duration: Breaks must be a minimum of 10 minutes for every 4 hours worked
When it comes to labor laws regarding breaks, it's essential to understand the duration of rest periods, especially for workers who log long hours. According to labor regulations, employees are entitled to a minimum of 10 minutes of break time for every 4 hours they work. This rule ensures that workers have adequate time to rest and recharge, preventing fatigue and promoting overall well-being.
The 10-minute break for every 4 hours worked is a standard practice to maintain productivity and employee health. During this break, workers can stretch, relax, or simply step away from their workstations to give their minds and bodies a much-needed respite. It is a legal requirement that employers must adhere to, as it directly impacts the quality of work and the overall satisfaction of their workforce.
This break duration is particularly crucial for jobs that require sustained concentration and physical effort. For instance, factory workers, healthcare professionals, and customer service representatives often work long shifts and benefit significantly from these mandatory breaks. By providing a 10-minute pause after every 4 hours, employers can ensure that their staff remain alert and focused, reducing the risk of errors and accidents.
It is important to note that this labor law applies to most employment situations, but there may be exceptions. For example, certain industries or roles might have different break schedules due to specific operational requirements. However, the core principle remains the same: workers should be granted a minimum of 10 minutes of break time for every 4-hour block of work.
In summary, the labor law mandating a minimum 10-minute break for every 4 hours worked is a vital aspect of employee rights and workplace safety. It ensures that workers have the necessary downtime to recover and maintain their productivity. Employers must be aware of this regulation to create a healthy and efficient work environment, ultimately benefiting both the company and its employees.
Joe Arpagio: Lawbreaker or Political Prisoner?
You may want to see also

Frequency: Employers must provide breaks at regular intervals throughout the workday
Breaks are an essential component of a healthy and productive work environment, and labor laws often mandate specific requirements regarding their provision. One of the most critical aspects of break regulations is the frequency of these pauses in the workday. Employers must ensure that employees are given regular intervals to rest and recharge, which can significantly impact overall job satisfaction and performance.
The frequency of breaks is a standard labor law that varies depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the work. In many countries, labor laws dictate that employees should be entitled to short breaks during their working hours. For example, in the United States, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) requires employers to provide a 10-minute rest break for every 4 hours of work. This break is crucial for employees to relax, stretch their legs, and briefly escape the demands of their tasks. Similarly, in the European Union, the Working Time Directive emphasizes the importance of regular breaks, suggesting a minimum of a 15-minute rest period for every 4-hour work period.
These mandated breaks serve multiple purposes. Firstly, they provide employees with a chance to rest and recover, reducing fatigue and improving focus. During these breaks, workers can step away from their desks or workstations, allowing their minds and bodies to rejuvenate. This is particularly important in jobs that require sustained concentration, as it can help prevent mental and physical exhaustion. Secondly, regular breaks encourage a healthier work-life balance. They allow employees to attend to personal needs, such as using the restroom, getting a drink, or even a quick snack, which can improve overall well-being.
Employers should be mindful of the timing and duration of these breaks. Breaks should be scheduled at regular intervals to ensure employees are not continuously working without a pause. For instance, a 30-minute break after every 2 hours of work can significantly enhance productivity and employee satisfaction. It is also essential to ensure that these breaks are not interrupted by non-essential tasks or meetings, as this can defeat the purpose of providing rest time.
In summary, labor laws emphasize the importance of providing breaks at regular intervals throughout the workday. These breaks are vital for employee health, productivity, and overall job satisfaction. Employers must be aware of the specific break requirements in their respective jurisdictions and ensure that their work schedules accommodate these mandatory rest periods. By doing so, employers can create a more positive and sustainable work environment for their employees.
Contract Breaches: Civil Law Violations?
You may want to see also

Enforcement: Violations can result in legal action and penalties
Enforcement of labor laws regarding employee breaks is a critical aspect of ensuring fair and safe working conditions. When employers violate these laws, it can lead to severe consequences, including legal action and penalties. Here's an overview of the enforcement process and the potential outcomes:
Legal Framework: Labor laws governing breaks vary by jurisdiction, but they generally aim to protect workers' health and well-being. These laws often mandate specific break durations, rest periods, and meal times. For instance, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) in the United States requires employers to provide a 10-minute rest break for every four hours of work, and a 30-minute break for every six hours. Violations of these regulations can be considered a breach of labor rights.
Enforcement Mechanisms: When a violation is reported or discovered, several enforcement mechanisms come into play. Firstly, labor departments or equivalent agencies are responsible for monitoring and enforcing these laws. They may conduct inspections, review employee records, and interview workers to gather evidence of potential violations. If a violation is confirmed, the employer may face legal consequences.
Legal Action: In cases of non-compliance, legal action can be taken against the employer. This may involve issuing warning letters, fines, or even lawsuits. For instance, if an employer consistently fails to provide rest breaks, the affected employees can file a complaint with the labor department, which may result in an investigation and subsequent legal proceedings. The severity of the penalty depends on the nature and frequency of the violation, as well as the jurisdiction's labor laws.
Penalties and Consequences: Penalties for break violations can be substantial. Fines are a common consequence, with amounts varying based on the severity and duration of the violation. In some cases, employers may be required to pay back wages to affected employees for the time they were denied breaks. Repeated or willful violations can lead to more severe penalties, including the suspension or revocation of business licenses, and even criminal charges in extreme cases.
Employee Rights and Support: It is essential for employees to understand their rights regarding breaks and rest periods. They should be aware of the labor laws in their region and know how to report any violations. Employee advocacy groups and labor unions can also play a crucial role in enforcing these rights, providing support to workers who have been affected by break violations.
Enforcement of labor laws related to breaks is a complex process, requiring collaboration between legal authorities, employees, and their representatives. By understanding the potential legal consequences, employers are more likely to comply, ensuring a healthier and more productive work environment for their employees.
Are 15-Minute Breaks Federally Mandated?
You may want to see also

Exceptions: Certain jobs may have different break requirements or none at all
In certain specialized fields, break regulations can vary significantly. For instance, in the emergency services sector, such as law enforcement or firefighting, officers often work in high-pressure, unpredictable environments. The nature of their jobs demands a high level of alertness and responsiveness at all times, leaving little room for traditional break periods. As a result, these professions may operate under different break protocols, prioritizing the need for continuous operational readiness over strict break schedules.
Similarly, outdoor workers, including farmers, gardeners, and construction laborers, face unique challenges. Their work is often physically demanding and exposed to the elements, requiring them to remain active throughout the day. In such cases, short, frequent breaks might be more beneficial than longer, less frequent ones to maintain productivity and safety. These jobs may have reduced break times or even no breaks at all, as the work environment and physical demands dictate a different approach to rest and recovery.
Another exception is found in the healthcare sector, particularly in emergency departments and intensive care units. Healthcare professionals in these settings often work in fast-paced, high-pressure environments where every second counts. The critical nature of their work may not allow for traditional break times, as patients require immediate attention and care. Healthcare providers in these roles might have different break requirements, focusing on short, frequent rest periods or even on-the-job breaks to maintain their energy and effectiveness.
Additionally, some jobs in the transportation industry, such as long-haul truck driving or maritime operations, fall into a unique category. These professions often involve extended periods of operation followed by mandatory rest periods. However, the nature of the work may require drivers to remain alert and ready to respond during these rest periods, ensuring the safety of the vehicle and its occupants. As such, break regulations for these jobs might be more flexible, allowing for varying break times or even on-duty rest periods to accommodate the demands of the job.
Lastly, certain manual labor jobs, like construction or heavy machinery operation, may have reduced break times due to the physical and mental demands of the work. These jobs often require workers to maintain a high level of concentration and physical exertion for extended periods, leaving little room for extended breaks. In such cases, short, frequent breaks might be more practical to ensure workers can quickly recover and maintain their performance.
Lunch Breaks: Understanding Your Rights as an Employee in New Jersey
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The number of breaks an employee is entitled to depends on various factors, including the duration of the shift and the industry. In many jurisdictions, employees are typically entitled to a 10-minute rest break for every 4 hours of work. However, specific regulations may vary, so it's essential to check the labor laws in your region.
The duration of a break can vary. For a 10-minute break, employees are usually allowed a short period to rest, relax, and use the restroom. Longer breaks, such as meal breaks, may be required in certain industries and jurisdictions, often lasting 30 minutes to an hour.
No, employers are generally not allowed to require employees to work during their scheduled breaks without their consent. If an employee is forced to work during a break, it may be considered an infringement on their rights and could lead to legal consequences for the employer.
Violations of labor laws related to breaks can result in various legal consequences. Employees may file complaints with labor authorities, and if found valid, the employer may face fines, penalties, or even legal action. It is essential for employees to be aware of their rights and report any violations to the appropriate authorities.
Yes, there can be exceptions. For example, in certain industries like healthcare or emergency services, employees may not be entitled to traditional rest breaks due to the nature of their work. Additionally, for employees working in roles that require continuous operation, break rules might be different. It's crucial to understand the specific regulations for your industry.







