Ballot propositions are new laws, constitutional amendments, or approvals of laws made by state legislatures. The process of getting a proposition on the ballot differs from state to state. In 24 states, the state legislature must vote to put a proposition on the ballot. In 26 other states, citizens may petition to put initiatives on the ballot. Each state places restrictions on the type of laws that can be considered or approved in a proposition. The initiative is the power of citizens to act as legislators in proposing statutes and amendments to the state constitution.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A suggested change or addition to the law of a state of the US, which citizens vote on |
| Citizen-driven ballot initiatives | Allow voters to petition for and vote on new state statutes, state constitutional amendments, and in some cases, overturn existing state laws in a referendum |
| Citizen-initiated referendum | Citizens may petition and vote on whether to uphold or strike down a law passed by a state legislature |
| Ballot measures by type | Initiatives, referendums, recalls |
| Ballot measures by topic | Statutes and amendments related to abortion access, measures related to elections, changes to the ballot proposition process |
| Requirements | A petition must get enough signatures of state residents to put the measure on the ballot |
| Signature requirements | Range from more than 997,000 signatures in California to just over 15,000 signatures in North Dakota |
| State legislature involvement | In 24 states, the state legislature must vote to put a proposition on the ballot |
| Number of propositions | 133 ballot propositions were voted on in 37 states and Washington, DC on Election Day 2022 |
What You'll Learn

A proposition is a suggested change to a law that citizens vote on
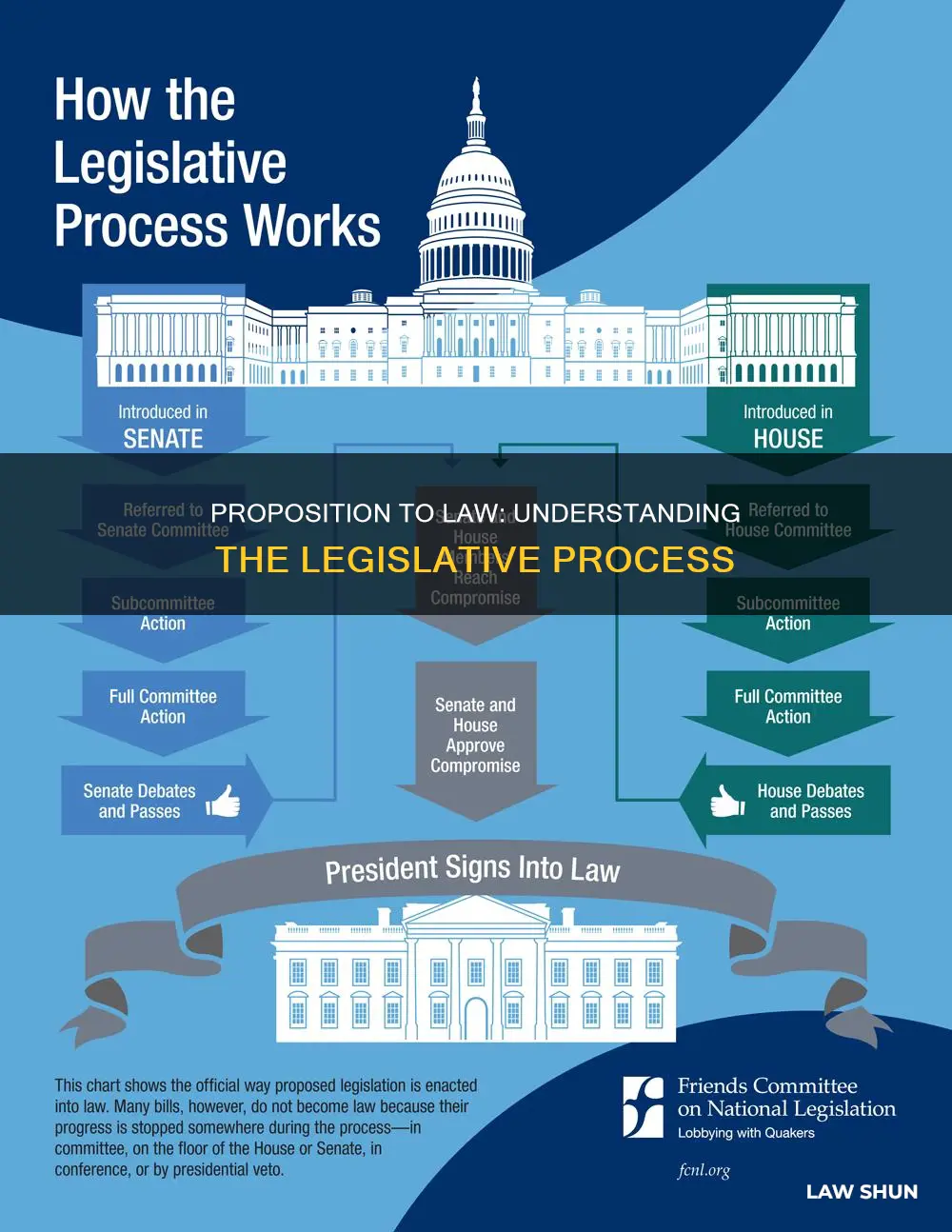
A proposition is a suggested change or addition to a law that citizens vote on. In the United States, ballot propositions are new laws, constitutional amendments, or approvals of laws made by state legislatures. All states allow citizens to vote on these propositions, but the process of getting a proposition on the ballot varies from state to state.
In 24 states, the state legislature must vote to put a proposition on the ballot. In the remaining 26 states, citizens may petition to put initiatives on the ballot. Each state places restrictions on what type of laws can be considered or approved in a proposition.
Citizen-driven ballot initiatives allow voters to petition for and vote on new state statutes and state constitutional amendments, and in some cases, to overturn existing state laws in a referendum. These initiatives usually start with a petition that must gather enough signatures from state residents to be placed on the ballot. The number of signatures required varies by state, ranging from over 997,000 in California to just over 15,000 in North Dakota. Once the petition is submitted, state officials verify the signatures to ensure they all belong to state residents.
The initiative process grants citizens the power to act as legislators by proposing statutes and amendments to their state's constitution. This process was established in 1911 as part of the Progressive Movement. Since then, there have been over 1,700 initiatives submitted, with about one-fifth qualifying for the ballot.
Understanding SNL's Satirical Take on How a Bill Becomes Law
You may want to see also

A proposition is introduced by people and voted on by people
A proposition is a suggested change or addition to a law, put forward by citizens, which citizens then vote on. In the United States, ballot propositions are new laws, constitutional amendments, or approvals of laws made by state legislatures. All states allow citizens to vote on these propositions, but the process of getting one on the ballot varies from state to state.
In 24 states, the state legislature must vote to put a proposition on the ballot. In the remaining 26 states, citizens may petition to put initiatives on the ballot. Each state places restrictions on what type of laws can be considered or approved in a proposition.
Citizen-driven ballot initiatives allow voters to petition for and vote on new state statutes, state constitutional amendments, and in some cases, overturn existing state laws in a referendum. These initiatives differ between states and start with a petition that must garner enough signatures from state residents to be put on the ballot. The number of signatures required varies from state to state, ranging from over 997,000 in California to just over 15,000 in North Dakota. Once the petition is submitted, state officials verify the signatures to ensure they all belong to state residents.
The process of qualifying a statewide initiative begins with the submission of a request (along with a fee) to the Attorney General's Office. During the first 30 days after submission, the public may provide comments to the initiative's proponents via a website operated by the Attorney General. The proponents may amend their measure at any time up to five days after this public comment period.
Understanding the Legislative Process: Bill to Law
You may want to see also

A proposition bypasses the legislature
In the United States, a proposition is a new law, a constitutional amendment, or an approval of a law made by state legislatures. While all states allow citizens to vote on these propositions, the process of getting one on the ballot varies from state to state.
In 24 states, the state legislature must vote to put a proposition on the ballot. However, in 26 other states, citizens can bypass the legislature by petitioning to put initiatives directly on the ballot. This is known as a citizen-driven ballot initiative or citizen-initiated referendum.
The rules for citizen-driven ballot initiatives differ between states. In California, for example, a petition must obtain enough signatures from state residents to put the measure on the ballot. The number of signatures required ranges from over 997,000 in California to just over 15,000 in North Dakota. Once the petition is submitted, state officials verify that all signatures belong to state residents.
After gaining approval, proponents in California have 180 days to gather the required number of signatures. They usually aim for at least 50% more than the legal minimum to compensate for any invalid signatures. Proponents who have gathered at least 25% of the required signatures must immediately submit a written statement to the Secretary of State, allowing time for each chamber in the State Legislature to assign the proposed initiative to its appropriate committees and schedule public hearings. However, it is important to note that the Legislature cannot amend the proposed initiative or prevent it from being added to the ballot once it qualifies.
In addition to citizen-driven ballot initiatives, citizens in 23 states and Washington, D.C., can also bypass the legislature through a citizen-initiated referendum. This process allows citizens to petition and vote on whether to uphold or strike down a law passed by a state legislature. Like ballot initiatives, referendums must gain enough signatures to be placed on the ballot.
The Evolution of Title IX: A Law's Journey
You may want to see also

A proposition is voted on in an upcoming election
A proposition is a suggested change or addition to the law of a state in the US, which citizens vote on. In 24 states, the state legislature must vote to put a proposition on the ballot. In 26 other states, citizens may petition to put initiatives on the ballot. Each state places restrictions on what type of laws can be considered or approved in a proposition.
The process of qualifying a statewide initiative begins with the submission of a request (along with a fee) to the Attorney General's Office. During the first 30 days after submission, the public may provide comments to the initiative's proponents. The proponents may amend their measure any time up to five days after this public comment period.
To qualify for the ballot, supporters must gather a specified number of valid signatures. Supporters then have a set number of days to gather signatures and turn them into the appropriate county elections office. Once the signatures have been certified by the Secretary of State, the measure goes on the next general election ballot.
Citizen-driven ballot initiatives allow voters to petition for and vote on new state statutes, state constitutional amendments, and in some cases, overturn existing state laws in a referendum. Citizen-driven ballot initiatives start with a petition that must get enough signatures of state residents to put the measure on the ballot. These signature requirements vary from state to state. Once the petition is submitted, state officials verify that all signatures belong to state residents.
Understanding the Lawmaking Process: A Simple Guide
You may want to see also

A proposition is easier to submit than a regular law
A proposition is a suggested change or addition to a law, put forward by citizens or state legislators, and voted on by citizens. The process of getting a proposition on the ballot differs from state to state in the US, but generally, it is easier to submit a proposition than a regular law.
In 24 states, the state legislature must vote to put a proposition on the ballot. This means that in almost half of US states, citizens do not have the power to initiate propositions themselves. However, in the other 26 states, citizens may petition to put initiatives on the ballot. This is done through a citizen-driven ballot initiative, which allows voters to propose and vote on new state statutes and constitutional amendments, and in some cases, overturn existing state laws through a referendum.
The process of a citizen-driven ballot initiative usually starts with a petition that must gather enough signatures from state residents to be put on the ballot. The number of signatures required varies from state to state, ranging from over 997,000 in California to just over 15,000 in North Dakota. Once the petition is submitted, state officials verify the signatures, and if enough valid signatures are gathered, the proposition is placed on the ballot for the next general election.
While the specific process and requirements for submitting a proposition vary across states, it generally provides a more accessible pathway for citizens to initiate changes or additions to laws compared to the traditional legislative process. This is because propositions allow citizens to bypass the state legislature and propose laws directly to their fellow citizens for a vote. This can be especially significant in states where the state legislature may be less responsive to the citizens' concerns or where certain issues may not receive adequate legislative attention.
Overall, while the submission and approval process for propositions can be complex and varies across states, it offers citizens a direct avenue to shape their state's laws and constitution. By gathering support and meeting the necessary requirements, individuals or groups can successfully initiate and pass propositions that reflect the values and needs of their communities.
The Lawmaking Process in North Dakota Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The initiative is the process that allows electors to propose legislation and compel the legislature or the full electorate to vote on the measure. A referendum is the power of the electors to approve or reject all or parts of certain types of statutes. Propositions are the proposed legislation for either the initiative or the referendum.
There are two kinds of propositions: legislative measures and initiative measures. Legislative measures are placed on the ballot by a majority vote from the state legislature. Initiative measures are proposed by non-politicians and must gather enough signatures of support from the public to be placed on the ballot.
Legislative measures can be legislative constitutional amendments, which seek to change parts of the constitution, or legislative statutes, which add or adjust laws that do not conflict with the state or federal constitution.
There are initiative constitutional amendments, which allow non-politicians to shape the constitution, and initiative statutes, which allow voters to amend statutes.
A referendum is a way for voters to approve or reject a statute enacted by the state legislature. Referendums are limited in scope and typically address issues involving government oversight. They are not allowed when laws relate to topics like elections, tax levies, or public emergencies.
The California Constitution requires the legislature to get voter approval before borrowing any amount above $300,000 in general obligation bonds. Bond measures ask voters to approve or deny spending for large projects such as water and education infrastructure.







