The US Senate is the upper chamber of Congress, with 100 members, two from each state serving six-year terms. The Senate has a wide range of powers and responsibilities, including proposing and amending legislation, confirming presidential nominees, approving treaties, and conducting impeachment trials. The Senate also has a role in educating the public and restraining the government through investigations of malfeasance in the executive branch. With such a broad remit, the Senate is a crucial component of the US government, and citizens can influence the legislative process through voting, advocacy, and direct communication with senators.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of senators | 100 (2 from each state) |
| Term | 6 years |
| Election | 1/3rd of the Senate is up for re-election every 2 years |
| Eligibility | 30+ years old, citizen of the US for 9+ years, resident of the state they represent |
| Powers | Proposing legislation, drafting or amending bills, filibustering, oversight of the federal budget, approving or rejecting presidential appointees for agencies, confirming presidential nominees to the federal judiciary and executive branch positions, approving treaties with foreign nations, convicting an executive or judicial official with a two-thirds vote in an impeachment trial, serving as a jury and judge in impeachment trials, conducting investigations of malfeasance in the executive branch and elsewhere in American society |
| Voting | Roll call votes, voice votes, unanimous consent, simple majority, two-thirds majority, three-fifths majority |
What You'll Learn
- The Senate can propose legislation and draft or amend bills
- Senators can delay or block legislation via a filibuster
- The Senate has the power to conduct impeachment trials
- Senators can vote in a variety of ways, including roll call votes and voice votes
- The Senate can confirm presidential nominees to the federal judiciary

The Senate can propose legislation and draft or amend bills
The Senate plays a crucial role in the legislative process, and its powers directly impact the lives of citizens. One of its key functions is proposing legislation and drafting or amending bills. This means that senators can introduce new laws or make changes to existing ones. Each state elects two senators, resulting in a total of 100 members in the Senate, and these senators serve six-year terms.
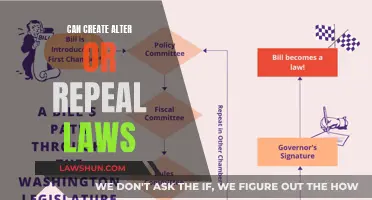
The process of proposing legislation begins with a senator introducing a bill to the Senate. Before a bill becomes a law, it must go through several steps. First, the Senate must agree to consider the bill by voting on a motion to proceed, which requires 60 votes. This is often a challenging hurdle to overcome, as senators may withhold their consent, indicating their opposition to the bill or a desire to delay its consideration.
Once the Senate agrees to consider a bill, it is referred to the relevant Senate committee for review. The committee may hold hearings, invite experts to testify, and make amendments to the bill. After the committee has finished its work, the bill is reported back to the full Senate for debate and a final vote. Senators can use procedures like filibuster to delay or block legislation via prolonged debate. However, the Senate can end a debate and invoke cloture with a three-fifths majority vote.
The Senate's power to propose legislation and draft or amend bills allows it to address complex challenges facing the nation and directly impact public policy. Citizens can influence this process by engaging with their senators, advocating for specific bills, and providing input on issues that affect their communities. By understanding the Senate's role in lawmaking, individuals can actively participate in democracy and ensure their voices are heard.
Municipal Laws and Cats: Who's in Control?
You may want to see also

Senators can delay or block legislation via a filibuster
To overcome a filibuster, the Senate can invoke cloture, which is a procedure that allows for the debate to be ended and a vote to be taken. Originally, invoking cloture required a two-thirds majority vote. However, over time, this threshold has been lowered to three-fifths (60 votes) of the 100-member Senate. In some cases, such as nominations to executive branch positions and federal judgeships, only a simple majority is required to end debate.
The use of the filibuster has evolved over time. In the past, a filibuster would completely halt all legislative activity in the Senate. However, the introduction of a two-track system in 1972 allowed the Senate to consider multiple pieces of legislation simultaneously, even in the face of a filibuster. This made it politically easier for the minority party to sustain a filibuster.
The filibuster has been used throughout history to delay or block legislation on a variety of issues, including civil rights, natural gas policy, and industrial relations laws. In recent years, there have been debates over whether to eliminate the filibuster or make further changes to the cloture rule. However, as of 2022, the filibuster remains a powerful tool for senators to influence the legislative process.
Can a Sitting President Face Legal Prosecution?
You may want to see also

The Senate has the power to conduct impeachment trials
The United States Constitution grants the Senate the sole power to conduct impeachment trials. The House of Representatives charges an official of the federal government by approving, by a simple majority vote, articles of impeachment. After the House of Representatives sends its articles of impeachment to the Senate, the Senate sits as a High Court of Impeachment to consider evidence, hear witnesses, and vote to acquit or convict the impeached official. The Senate's impeachment rules have remained largely the same since their adoption during the trial of President Andrew Johnson.
The Senate has the power to convict an executive or judicial official with a two-thirds vote in an impeachment trial. The penalty for an impeached official upon conviction is removal from office. In some cases, the Senate has also disqualified such officials from holding public offices in the future. The conviction is not a punishment, and the president of the United States is constitutionally prevented from granting a pardon to impeached and convicted persons.
The Senate has a long history of using the filibuster to delay debate or block legislation. Unlimited debate remained in place in the Senate until 1917, when the Senate adopted Rule 22, allowing the Senate to end a debate with a two-thirds majority vote, a procedure known as "cloture." In 1975, the Senate reduced the number of votes required for cloture from two-thirds (67) to three-fifths (60) of the 100-member Senate.
Since 1789, the Senate has tried 20 federal officials, including three presidents. On April 17, 2024, the Senate trial for the impeachment of Alejandro Mayorkas, the Cabinet Secretary of Homeland Security, was unprecedented. The trial proceedings ended quickly as, after the jurors were sworn in, the Senate dismissed the accusations, agreeing that the articles of impeachment did not comply with the United States Constitution.
Scientific Laws: Immutable or Evolving?
You may want to see also

Senators can vote in a variety of ways, including roll call votes and voice votes
The Senate is considered the upper chamber of Congress, with 100 members, two from each state. Senators are elected to serve six-year terms and are part of the Legislative branch of the government. They have a variety of constitutional powers, including proposing legislation, drafting or amending bills, and overseeing the federal budget.
Senators can vote in a variety of ways, including roll call votes, voice votes, and unanimous consent. A roll call vote is a vote in which each senator's name is called, and they respond with their vote. This type of vote is typically used for important or controversial issues and provides a public record of how each senator voted. On the other hand, a voice vote is a vote in which senators simply voice their support or opposition to a measure, and the presiding officer announces the result based on the volume of voices. This type of vote is often used for non-controversial or routine matters and helps expedite the legislative process.
Additionally, unanimous consent is another voting method where the majority and minority leaders seek consent from all senators to pass legislation without a roll call vote. This method is used for non-controversial bills to save time and expedite the legislative process. However, if any senator withholds their consent, they can implicitly threaten an extended debate on the bill. This tactic can be used to delay consideration of a measure or influence the fate of an unrelated measure.
The Senate also has the power to confirm presidential nominees to the federal judiciary and executive branch positions. In this process, a simple majority vote is usually required for confirmation, but nominations are debatable, and supporters may need to use the cloture process to reach a vote. The cloture process requires a three-fifths majority vote to end debate and proceed to a vote, and it can be a lengthy procedure.
Overall, the Senate's voting procedures are crucial in shaping legislation and confirming nominees, and senators have several methods to influence the legislative process.
Elder Law Attorneys: Navigating Medicaid Applications
You may want to see also

The Senate can confirm presidential nominees to the federal judiciary
The U.S. Constitution grants the Senate the power to confirm presidential nominees to the federal judiciary, including the Supreme Court. This process, known as the "advice and consent" of the Senate, is outlined in Article 2, Section 2 of the Constitution. The Senate plays a crucial role in shaping the political landscape of the Supreme Court by considering a range of factors when deciding whether to confirm a nominee. These factors include political considerations, the nominee's judicial philosophy, fitness for the bench, past statements on relevant issues, and the overall balance of power between political factions.
The Senate has the authority to hold confirmation hearings for Supreme Court nominees, where nominees may be questioned by Senators. These hearings can be quite contentious and last for months, as was the case with the nomination of Harlan Fiske Stone in the early 20th century. Since 1955, the Judiciary Committee has held open hearings for all Supreme Court and lower court nominees, allowing for increased scrutiny of the candidates.
The confirmation process can be influenced by various factors, such as the timing of a Supreme Court vacancy and public opinion of the President. For example, a vacancy occurring shortly before an election may impact the type of candidate that can be confirmed. Additionally, a President with strong approval ratings may have an easier time achieving confirmation for their preferred nominees.
The Senate's role in confirming presidential nominees to the federal judiciary is an essential check and balance in the U.S. political system, ensuring that the President's appointments are suitable and qualified for their respective roles.
Who Can Give Lawful Orders? Understanding an NCO's Authority
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Senate is the upper chamber of Congress and has full legislative authority. Senators propose legislation, draft or amend bills, and vote on them. They can also delay or block legislation via a filibuster, which is a prolonged debate.
The Senate has the power to approve or reject presidential appointees for agencies. They also approve the federal budget.
The Senate approves treaties with foreign nations negotiated by the Executive Branch. The Constitution requires a two-thirds vote for a treaty to be ratified.
The Senate has the sole power to conduct impeachment trials, serving as both jury and judge. They can convict an executive or judicial official with a two-thirds vote.
The Senate is made up of 100 members, with each state electing two senators for six-year terms. Citizens can influence the legislative process by voting, advocacy, or direct communication with senators and their staff.