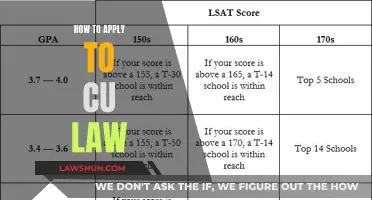
Applying the law is a complex process that involves various steps and considerations. When a court applies the law, it interprets and enforces a set of rules, statutes, principles, or policies. The process typically begins with the introduction of a bill, which is a proposal for a new law or a change to an existing law. This bill is then assigned to a committee that researches, discusses, and makes changes to it. The bill is then presented to the legislative body for a vote, and if passed, it goes through a similar process in the other chamber. Once both chambers approve the bill, they work together to resolve any differences and vote on the final version. If the bill passes this stage, it is sent to the executive for approval, typically by the president or head of state. If approved, the bill becomes a law. However, if the executive vetoes the bill, the legislature may still be able to override the veto and pass the bill into law.
The application of the law also involves interpreting existing laws and ensuring they are applied fairly and consistently. This is where the concept of the rule of law comes into play. The rule of law is a fundamental principle that holds that all persons, institutions, and entities are accountable to laws that are publicly promulgated, independently adjudicated, and consistent with human rights principles. Courts play a crucial role in maintaining the rule of law by interpreting laws and ensuring they are applied justly and impartially. This includes interpreting the constitution and ensuring that any laws passed by the legislature do not conflict with it.
The process of applying the law can be further understood through the concepts of inferential law-application and pragmatic law-application. Inferential law-application involves reasoning and drawing conclusions about a specific case based on existing laws. On the other hand, pragmatic law-application refers to the actual performance of an action or decision by a court, which is legally justified by reference to the relevant laws. These two concepts are closely related, as pragmatic law-application builds upon the conclusions reached through inferential law-application.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Rule of law | A durable system of laws, institutions, norms, and community commitment |
| Accountability | The government and private actors are accountable under the law |
| Just Law | The law is clear, publicized, stable, and applied evenly |
| Open Government | The processes by which the law is adopted, administered, adjudicated, and enforced are accessible, fair, and efficient |
| Accessible and Impartial Justice | Justice is delivered in a timely manner by competent, ethical, and independent representatives who have adequate resources and reflect the makeup of the communities they serve |
| Direct object of law-application | Statutes, rules, principles, policies, doctrines, other courts' views, etc. |
| Indirect object of law-application | Cases, facts, the facts of the particular case |
| Content of law-application | A specific type of act |
What You'll Learn
- The role of criminal law in addressing white-collar crime and corporate wrongdoing
- The legal and ethical implications of police use of force and accountability
- The legal and social consequences of wrongful convictions and the importance of due process
- The role of plea bargaining in criminal law and its impact on the justice system
- The impact of racial and socioeconomic factors on criminal justice outcomes

The role of criminal law in addressing white-collar crime and corporate wrongdoing
Criminal law plays a crucial role in addressing white-collar crime and corporate wrongdoing, which often overlap and result in significant financial losses and harm to victims and the broader community. White-collar crime, typically perpetrated by individuals or entities from the middle or upper classes, includes a range of non-violent offences committed for financial gain, such as fraud, bribery, embezzlement, and money laundering.
The effective application of criminal law in this context is essential to hold perpetrators accountable, deter future crimes, and restore justice for those affected. Criminal law provides a framework to investigate, prosecute, and sanction individuals and corporations involved in white-collar crimes. It establishes clear and stable standards and penalties to address these offences, aiming to protect society from financial and economic harm.
However, the prosecution of white-collar crime and corporate wrongdoing can be challenging due to the sophisticated means used by perpetrators to conceal their activities. Additionally, the complexity of these cases and the involvement of high-ranking corporate officers require specialised knowledge and resources for effective investigation and prosecution.
To address these challenges, various measures can be implemented. These include enhancing the capabilities of law enforcement agencies, fostering whistleblowing, and international cooperation to tackle transnational aspects of white-collar crime. The successful application of criminal law in this context helps maintain public trust in the justice system and ensures that those who engage in white-collar crime and corporate wrongdoing are held accountable, regardless of their social status or position.
Anti-Money Laundering Laws: Annuities and Compliance
You may want to see also

The legal and ethical implications of police use of force and accountability
The application of the law is a complex and dynamic process that involves legal and ethical considerations. In the context of police use of force, understanding the legal and ethical implications is crucial for ensuring accountability, transparency, and the protection of individual rights.
Legal Implications
The legal framework governing police use of force is deeply rooted in constitutional principles, statutes, and law enforcement policies. The Fourth Amendment, enshrined in the Bill of Rights, safeguards individuals from unreasonable searches and seizures, establishing the parameters for the lawful application of force. Federal and state laws further delineate the guidelines for the use of force, with each state having its own legal framework. Law enforcement agencies formulate their own use-of-force policies, which reflect a commitment to align with national standards and ensure a consistent and standardized approach.
Ethical Implications
The ethical framework for police use of force is guided by professional standards and conduct outlined in the Code of Ethics for Law Enforcement. This code emphasizes the responsible use of force, upholding the law impartially, and respecting the rights of all individuals. Ethical considerations extend beyond the moment of force application to include accountability, transparency, and thorough reporting and documentation of use-of-force incidents. Internal Affairs investigations play a pivotal role in ensuring accountability, subjecting incidents to rigorous scrutiny.
Factors Influencing Police Use of Force
The decision to use force is influenced by various factors, including the behavior of the suspect, the level of resistance, the presence of weapons, and the threat to public safety. Officers must assess the level of threat posed, considering factors such as aggression and the perceived intent to harm. Comprehensive training is essential to ensure accurate interpretation and response to dynamic situations, enhancing situational awareness, de-escalation techniques, and decision-making skills.
Impact of Police Brutality
Police brutality has far-reaching consequences, affecting both individuals and communities. It erodes public trust in law enforcement, undermines the legitimacy of police forces, and strains relationships between marginalized communities and the police. Incidents of police brutality result in psychological, social, and emotional repercussions for victims and their communities, highlighting the need for healing, accountability, and justice.
Mechanisms for Police Accountability
Ensuring accountability for police misconduct is crucial for maintaining public trust. Internal Affairs investigations, civilian oversight boards, disciplinary procedures, criminal prosecutions, and civil litigation are mechanisms in place to address instances of excessive force. However, their effectiveness has been questioned due to factors like bureaucratic delays and a lack of transparency.
Scooters and the 7500-Mile Law: What's the Verdict?
You may want to see also

The legal and social consequences of wrongful convictions and the importance of due process
The application of law is a complex process that carries significant weight and consequences. When it comes to the topic of wrongful convictions, the legal and social implications can be far-reaching, underscoring the critical importance of due process.
Wrongful convictions, where an individual is found guilty of a crime they did not commit, have serious repercussions not only for the wrongfully accused but also for the original victims of the crime, their families, and the wider community. The impact of a wrongful conviction can be devastating, as innocent people may face imprisonment, loss of reputation, and psychological trauma. The original victims of the crime may experience feelings of guilt, fear, helplessness, and even depression when the wrong person is convicted. This can be further exacerbated by the media attention that often surrounds such cases, leading to a sense of being revictimized and a violation of privacy.
To safeguard against wrongful convictions, the legal system upholds the principle of due process, which emphasizes fair treatment and the protection of individual rights throughout the criminal justice process. Due process ensures that all legal proceedings are conducted justly and impartially, reducing the risk of errors and safeguarding against arbitrary decisions by authorities. It promotes rigorous standards for evidence gathering and trial procedures, helping to prevent miscarriages of justice.
Procedural due process, as outlined in the Fifth and Fourteenth Amendments to the U.S. Constitution, ensures that certain steps are taken before depriving an individual of life, liberty, or property. This includes the right to notice, an opportunity to be heard, an unbiased decision-maker, the right to present evidence, and the right to cross-examine opposing witnesses, among other protections.
Additionally, substantive due process protects certain fundamental rights deeply rooted in American history and tradition, such as reproductive rights, LGBTQ+ rights, and end-of-life decisions. This aspect of due process requires strict scrutiny of government actions that affect these fundamental rights, ensuring that any infringement serves a compelling government interest and is narrowly tailored to achieve that specific interest.
The importance of due process in preventing wrongful convictions cannot be overstated. By adhering to the principles of due process, the legal system strives to minimize errors, protect the rights of the accused, and uphold the integrity of the justice system as a whole. It is a crucial safeguard that helps maintain public trust and confidence in the fairness and effectiveness of the law.
In conclusion, wrongful convictions have far-reaching legal and social consequences, underscoring the critical importance of due process. By prioritizing fair treatment, protecting individual rights, and adhering to rigorous standards, the legal system can help prevent miscarriages of justice and ensure that justice is served for all.
Civil Law and Medical Assistants: Understanding the Legal Boundaries
You may want to see also

The role of plea bargaining in criminal law and its impact on the justice system
Plea bargaining is a common feature of the US criminal justice system, with 90-98% of criminal cases ending in a plea bargain. In a plea bargain, the defendant agrees to plead guilty or no contest in exchange for concessions from the prosecution. These concessions may include a reduction in the level of the charge, a recommendation for a more lenient sentence, or a reduction in the number of charges.
Plea bargaining has been criticised for prioritising efficiency over fairness and innocence, leading to innocent people being coerced into guilty pleas. The power prosecutors hold over defendants, including the threat of decades-long mandatory minimum sentences, can result in defendants pleading guilty to avoid harsher punishments. This can result in police and government misconduct going unchecked, as mistakes and misbehaviour often only come to light during a trial.
Plea bargaining also exacerbates racial inequality, with Black defendants more likely to face stacking of multiple charges in drug and gun cases, leading to stiffer punishments for going to trial. In addition, defendants who plead guilty are left with a permanent criminal record, which can impact their civil rights and future prospects.
However, plea bargaining can also be beneficial for defendants, allowing them to move forward with their lives and avoid the uncertainty and cost of a trial. Defendants may also be able to seal or expunge their criminal record more easily after a plea bargain. In addition, plea bargaining can help to reduce the burden on the criminal justice system, allowing prosecutors and judges to focus their time and resources on more complex cases.
Overall, while plea bargaining plays a significant role in the US criminal justice system, there are valid concerns about its impact on fairness, innocence, and racial inequality. Reforms are needed to ensure that the process is fair and just for all defendants.
Discrimination and the Law: Understanding Your Rights
You may want to see also

The impact of racial and socioeconomic factors on criminal justice outcomes
Laws are applied through a process that involves multiple entities and stages. In the United States, laws are created by the legislative branch, which includes Congress, through a lawmaking procedure. Once a bill is introduced, it goes through a process of research, discussion, amendment, and voting in both the Senate and the House of Representatives. If the bill passes in both chambers, they work together to resolve any differences, and a final vote is held. The bill is then presented to the President for approval or veto. If vetoed, Congress can override the veto, and the bill becomes law. This process ensures that laws are established through careful consideration and deliberation.
Once laws are in place, they are applied in various contexts, such as policing, court proceedings, and correctional systems. The impact of racial and socioeconomic factors on criminal justice outcomes is a significant concern within the application of laws. Racial and socioeconomic disparities within the criminal justice system refer to the unequal treatment and outcomes experienced by individuals based on their race, ethnicity, or economic status. This issue challenges the principle of equality before the law, which is fundamental to democratic societies.
Racial and socioeconomic factors have a profound influence on criminal justice outcomes, from policing to sentencing and incarceration. Socioeconomic status (SES), encompassing income, education, and occupational prestige, plays a pivotal role in shaping individuals' experiences and trajectories within the legal system. Individuals from different socioeconomic backgrounds may face divergent patterns of police engagement, with factors such as neighborhood demographics and access to education influencing the nature and frequency of interactions with law enforcement.
Racial profiling, bias in charging and prosecution decisions, and disparities in sentencing further contribute to unequal outcomes. Studies have consistently shown that minority groups, particularly African Americans and Hispanics, are overrepresented at every stage of the criminal justice process. Socioeconomic factors also impact access to legal resources and representation, with individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds facing harsher treatments due to limited access to quality legal representation.
The consequences of these disparities are far-reaching. They affect not only the individuals involved but also their families and communities, leading to higher incarceration rates, longer sentences, and more severe legal penalties. Additionally, the over-policing of certain communities contributes to a cycle of disadvantage and mistrust towards law enforcement, hindering community relations and exacerbating social tensions.
To address these disparities, various reform initiatives and policies have been implemented. Legislative changes, such as reducing mandatory minimum sentences for non-violent drug offenses, and bail reform initiatives, aim to mitigate the impact of economic status on pretrial detention and sentencing. Community-based programs, such as restorative justice initiatives and community policing, focus on rehabilitation and building trust between law enforcement and marginalized communities.
In conclusion, the application of laws is a complex process that involves multiple stages and entities. Racial and socioeconomic factors significantly shape criminal justice outcomes, and addressing these disparities is crucial for upholding the principles of justice, equality, and fairness in democratic societies.
Maximizing Performance with Amdahl's Law: A Practical Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The rule of law is a system of laws, institutions, norms and community commitment that delivers four universal principles: accountability, just law, open government, and accessible and impartial justice.
Courts take the position that the legislature does not want to promulgate ineffective laws. So, the starting point for the analysis is to find a way of reading the law so that any conflict is eliminated or, at the very least, minimised.
It depends on the law and the jurisdiction. In some cases, there may be legal consequences such as fines or imprisonment. In other cases, the law may be enforced by a government agency or through private legal action.
The federal courts are responsible for interpreting the Constitution and any laws passed by Congress. They ensure that the people's representatives act only within the authority given to them by the Constitution.